Your cart is currently empty!
Rheumatism Tea
Long Leaf Rheumatism Tea
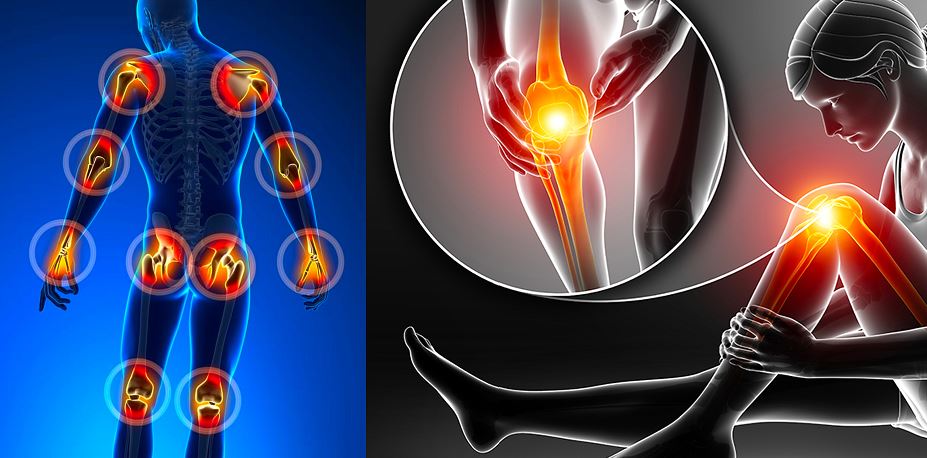

Rheumatism Arthritis Tea
The role of herbs in the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), has gained increasing attention in recent years. A growing number of studies have focussed on the diverse nutritional contents of herbs, and their possible role in the development and progression of RA. Herbs have a key role within the mosaic of autoimmunity in RA and potential to alter the microbiome, leading to downstream effects on inflammatory pathways. The molecular contents of herbs and tea have similarly been found to interfere with immune signalling pathways, some beneficial for disease progression and others less so.
What’s Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic, immune-inflammatory disease, with a complex aetiology, including genetic, environmental, and endogenous triggers . Factors such as cigarette smoking, infectious agents, environmental pollution, and chronic stress have been cited as possible triggers for the intense inflammatory response and production of pro-inflammatory mediators seen in RA . In recent years, there has been increasing evidence for the role of herbs and tea in RA disease onset and activity, although this has failed to filter down to clinical awareness and practice as an adjunct to pharmacological treatments . This includes the important role played by herbs and tea.
Herbs and tea which are enjoyed in abundance around the world. With over 20,000 varieties of tea, these drinks are integral to many cultures, each with their own unique nutritional profile.
Tea and herbs have multiple effects on human health through a variety of mechanisms. As mentioned previously, dietary phenols in both tea and coffee are able to alter DNA methylation, with downstream effects on factors including inflammation and oestrogen metabolism. However, the anti-inflammatory properties of rheumatism tea span far beyond the epigenome.
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), the main phytochemical and flavonoid-containing catechin present in green tea (Camellia sinensis), has gained significant attention in recent years in areas as wide ranging as anti-angiogenesis in the setting of malignancy to cardiovascular disease. Protective effects in the setting of autoimmune disease have also been studied. EGCG inhibits CD4+ T cell expansion in response to polyclonal or antigen-specific stimulation, as well as impeding Th1 and Th17 differentiation through downregulation of their transcription factors (STAT1 and T-bet for Th1, and STAT3 and RORγt for Th17), corresponding with reduced clinical symptoms in mouse models of multiple sclerosis (As the photo below). The balance of Th17 and Treg is crucial in the pathogenesis of RA, which may partly explain the benefits of EGCG consumption in this disease. Green tea extract reduces chemokine production in RA synovial fibroblasts leading to decreased inflammation, as well as modestly ameliorating adjuvant-induced arthritis in rat models. In addition, the catechin epigallocatechin gallate (EGC), works synergistically with EGCG to inhibit IL-6, IL-8, and MMP-2 production and selectively inhibits COX-2 expression . However, not all catechins in green tea appear to be equal, as demonstrated by epicatechin (EC), which, in this same study, was shown to hinder the marked downstream inflammatory signalling inhibition exerted by EGCG.
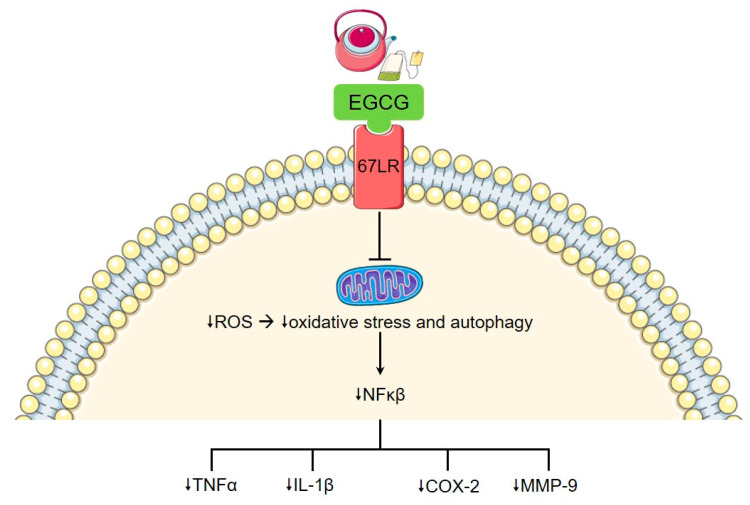
Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on inflammation. EGCG modulates intracellular signalling pathways via the 67 kDa laminin receptor (67LR). This reduces mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species, leading to reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine production, including NFκβ. This has multiple downstream effects, including downregulation of TNFα, IL-1β, cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2), and matrix metalloproteases (MMP), such as MMP-9.
Remember, while natural remedies like Rheumatism Arthritis tea can be beneficial, they should be approached thoughtfully and in conjunction with medical advice. Please notice that natural remedies like herbs and tea is not surrenal nor alternative of medication, always take it as a supplement of medication.
Long Leaf is not confined to the past and tradition—we are passionate about the cutting edge innovation shaping our recipe of tea and herbs today.
Green Tea, Ginger Tea with honey flavor, mint flavour, Lemon flavor, detox tea, slim beauty and abdominal slimming tea, heart protecting tea, hypertension tea, Ginseng Tea, Kidney Tea, Blood cleansing Tea, Lung Cleansing Tea, Diabetes Tea, Gout Tea, Beauty Tea, Liver Nourishing Tea, Rheumatism Tea, Sex Tea, Kuding Tea.We distribute our tea in South Africa (Johannesburg, Pretoria, Cape Town, Durban, East London), Botswana, Namibia, Mozambique, Swaziland, Congo, Zambia, Malawi, Lesotho.
